I’ve lived in Georgia my whole life and love the red clay soil. It covers the state’s hills and valleys. This soil has shaped Georgia’s history, culture, and economy for centuries.
Whether you garden, farm, or just love nature, learning about Georgia’s red clay is key. It’s a story worth telling.
Why do so many Georgians adore this soil? Its unique look and deep impact on the land make it special. Let’s explore this amazing natural treasure together. We’ll see how it defines Georgia.
Table of Contents
What Type of Soil Is Georgia Known For?
Georgia’s soil is a unique and defining feature of the state’s landscape. At the heart of this rich earth is the iconic red clay soil. It has captivated residents and visitors for generations.
This distinctive soil type is the result of centuries of geological processes. It plays a vital role in the state’s ecosystem, agriculture, and cultural identity.
Characteristics of Red Clay Soil
Georgia’s red clay soil is made of fine, tightly-packed particles. This gives it a unique texture and properties. It is known for its excellent water retention, holding onto moisture well.
However, the compact nature of red clay can lead to challenges. It can become easily compacted, and drainage can be impaired.
How Red Clay Forms
The red color of Georgia’s soil comes from iron oxides. These are formed through the weathering of feldspar and mica-rich rocks over time. This weathering, combined with the state’s warm, humid climate, has created the nutrient-rich soil composition georgia we see today.
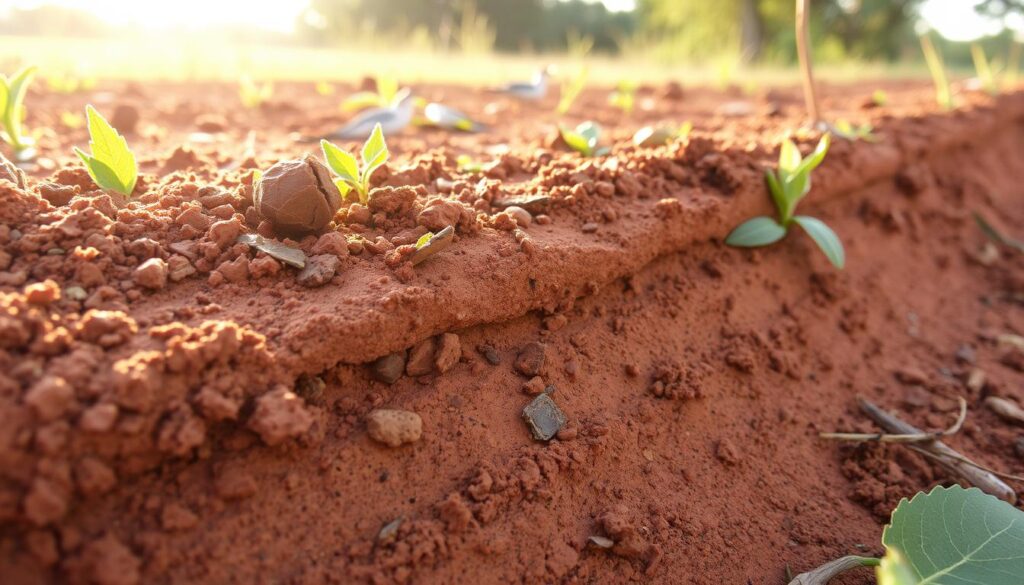

“The red clay soil of Georgia is a testament to the region’s rich geological history and the resilience of its ecosystems.”
Understanding Georgia’s red clay soil is key to appreciating the state’s natural resources. It helps us understand the challenges faced by gardeners and farmers in cultivating this distinctive earth.
Historical Significance of Georgia Soil
Georgia’s soil has been key in shaping the state’s history. It has influenced everything from Native American farming to early colonial settlements. The soil’s unique qualities have deeply impacted the region’s growth.
Soil in Native American Agriculture
Before European settlers came, Native Americans knew the land well. The georgia agriculture soil was perfect for growing corn, beans, and squash. These crops were the base of their farming.
This rich soil helped Native American communities grow and live sustainably. It was a crucial part of their way of life.
Impact on Early Colonial Settlements
When Europeans first arrived, they found the georgia soil management tough. The red clay soil was very different from what they knew. It needed new farming methods.
The soil’s ability to hold water and its fertility shaped early settlements. This influenced the state’s growth and economy.
Today, Georgia’s soil is still important. The state is a top agricultural producer. It shows the lasting effect of this valuable resource.
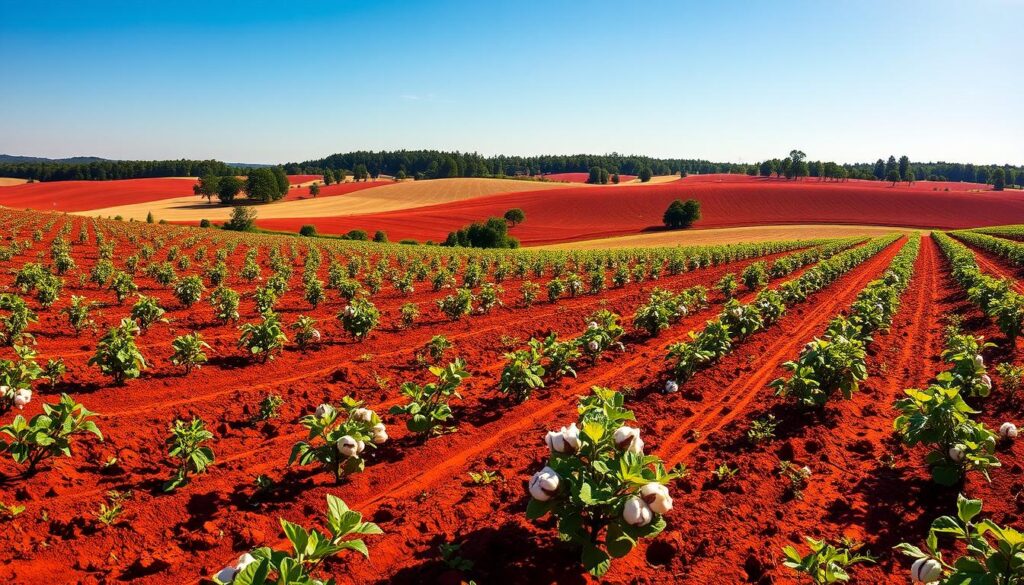

Types of Soil Found in Georgia
Georgia’s landscape is diverse, showing in its soil types. From sandy coastal soils to rich red clay in the Piedmont, and rocky northern mountains, each supports unique ecosystems and farming.
Sandy Soil in Coastal Regions
The coastal areas of Georgia have sandy soils. These are perfect for growing peanuts, sweet potatoes, and some vegetables. Sandy soils drain well and have less nutrients, making them great for certain crops.
Loamy Soil in the Piedmont
The Piedmont region is known for its fertile soil georgia, or “red clay” soil. This soil is rich in nutrients and good for many crops like cotton, peaches, and grains. The georgia soil types here have lots of clay, keeping moisture and nutrients in.
Clay Soil in the Northern Mountains
In Georgia’s northern mountains, the soil is a mix of clay and rock. This soil can be hard for farming, but it supports special ecosystems. These ecosystems thrive in the mountains’ cooler, wetter conditions.
| Soil Type | Region | Characteristics | Suitable Crops |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soil | Coastal Regions | Well-drained, low in nutrients | Peanuts, sweet potatoes, vegetables |
| Loamy Soil (Red Clay) | Piedmont | Nutrient-rich, high in clay | Cotton, peaches, grains |
| Clay and Rocky Soil | Northern Mountains | Challenging for agriculture, supports unique ecosystems | Limited agricultural potential |
The different georgia soil types across the state make each region unique. They offer various opportunities and challenges for farming.

Benefits of Red Clay Soil
Georgia’s red clay soil is a treasure for gardeners and farmers. It’s dense but drains well and keeps nutrients. This makes it perfect for many plants, from fruit trees to flowers.
Excellent Drainage Properties
Red clay soil in Georgia drains water well. Its clay content controls water flow, avoiding waterlogging. This is great for fruit trees that need good drainage.
Nutrient Retention Capacity
Georgia’s red clay soil also holds onto nutrients well. Its clay content keeps minerals and organic matter for plants. This makes it ideal for many crops that need rich soil.
| Fruit Tree | Recommended Variety | USDA Hardiness Zones |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | – | 5-8 |
| Pear | Requires two varieties for cross-pollination | 5-9 |
| Plum | Grafted onto St. Julian A rootstock | 6-10 |
| Cherry | ‘Bing’ variety | 5-8 |
| Persimmon | – | 4-9 |
| Fig | – | 6-11 |
| Mulberry | – | 4-8 |
| Quince | – | 4-9 |
| Peach | ‘Harcot’, ‘Goldrich’ | 5-8 |
| Nectarine | – | 5-8 |
| Apricot | ‘Harcot’, ‘Goldrich’ (cold regions), ‘Moorpark’ (warm areas) | 4-9 |

“The cement industry accounts for an estimated 7% of the total carbon dioxide emissions annually, and producing one ton of cement requires approximately 5.6 GWh of energy.”
Knowing the benefits of Georgia’s nutrient-rich soil helps gardeners and farmers. They can grow a wide variety of plants. The soil’s drainage and nutrient retention are key advantages for those who use it well.
Challenges of Red Clay Soil
Georgia’s red clay soil is known for its great drainage and ability to hold nutrients. Yet, it also brings challenges for gardeners and farmers. Knowing these challenges is key to growing crops well and keeping the soil healthy.
Erosion Concerns
Red clay soil is prone to erosion, especially on slopes. Its dense nature makes it easy for rain or wind to wash it away. This can cause the loss of topsoil and nutrients, harming plant growth and soil health.
Nutrient Deficiency Issues
Even though red clay soil holds nutrients well, it can lack some like phosphorus and nitrogen. This is because the soil can “fix” these nutrients, making them hard for plants to get. To fix this, adding organic matter and specific fertilizers is important.
| Nutrient | Typical Levels in Red Clay Soil | Recommended Amendments |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphorus (P) | Low to moderate | Bone meal, rock phosphate, or superphosphate |
| Nitrogen (N) | Moderate to high | Compost, manure, or nitrogen-rich fertilizers |
| Potassium (K) | Moderate to high | Greensand, wood ash, or potassium sulfate |
Understanding the challenges of managing red clay soil in Georgia helps gardeners and farmers. They can then find ways to overcome these issues. This ensures their land stays productive and healthy for a long time.
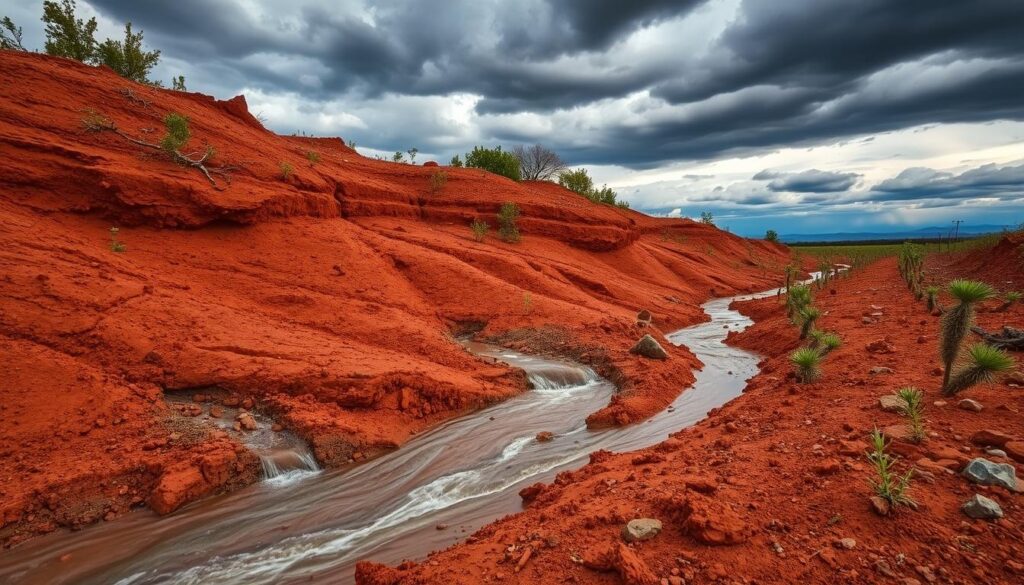

“Addressing the challenges of red clay soil is essential for sustainable agriculture in Georgia. With the right management techniques, this unique soil can be transformed into a productive and thriving ecosystem.”
Gardening in Georgia’s Red Clay
Georgia’s red clay soil can be tough for gardeners, but you can still grow a beautiful garden. The secret to georgia soil management is to add organic matter and choose the right plants. This way, your garden will flourish.
Soil Amendments for Better Growth
Red clay soil is dense, which can slow down roots and water. To fix this, add compost, peat moss, or well-rotted manure. These help the soil drain better, hold more nutrients, and keep water longer.
Building raised garden beds is also a smart move for fertile soil georgia. They make it easier for plants to grow by providing better drainage and nutrients.
Planting Strategies for Success
- Choose plants native to Georgia. They need less care and do well in the local climate and soil.
- Use French drains or gravel to prevent water from pooling. This keeps your plants healthy.
- Spread mulch around your plants. It keeps the soil moist and stops weeds from growing. Pine bark, leaf litter, or wood chips work great.
With some effort, you can make a stunning garden in Georgia’s red clay. Knowing how to handle this soil and using the right gardening tips will lead to a lush, vibrant space.
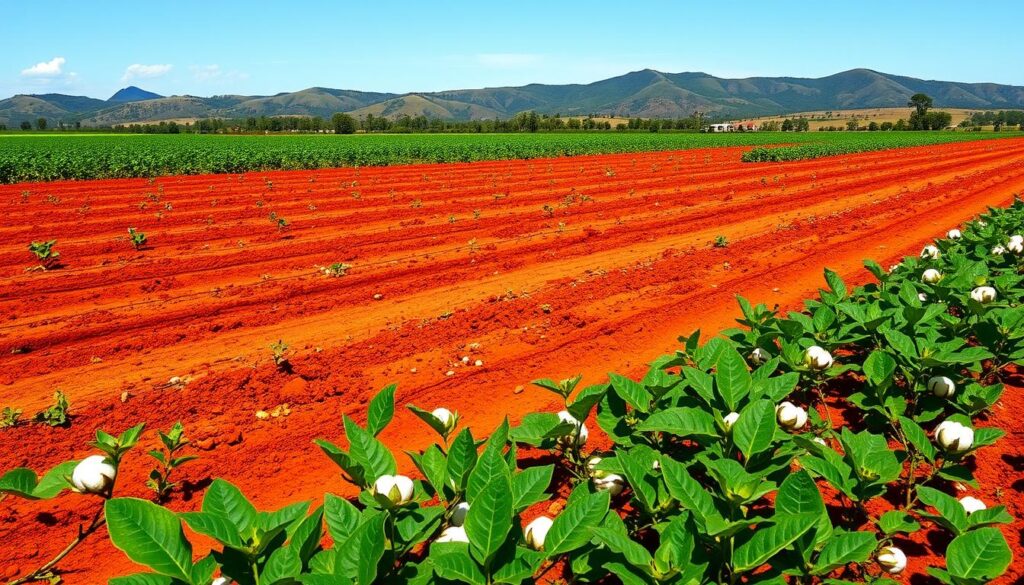
Farming Practices in Georgia
Georgia’s rich, fertile georgia agriculture soil has long been a boon for the state’s thriving agricultural industry. From the iconic cotton fields to the diverse array of crops that thrive in the fertile soil georgia, Georgia’s farmers have honed their practices to make the most of the region’s unique soil characteristics.
Crops Well-Suited for Red Clay
The red clay soil that blankets much of Georgia is particularly well-suited for growing a variety of crops, including:
- Cotton – Georgia is one of the nation’s leading cotton producers, with over two million bales harvested in 2023 using modern, GPS-guided machines.
- Soybeans – This legume crop thrives in the nutrient-rich red clay, with Georgia ranking among the top soybean-producing states.
- Peaches – Georgia’s famous peach orchards flourish in the clay-based soil, producing some of the sweetest and juiciest fruit in the country.
Sustainable Agriculture Techniques
Recognizing the importance of preserving the health and fertility of their georgia agriculture soil, many Georgia farmers have adopted sustainable agriculture practices, including:
- Crop Rotation – Rotating different crops through their fields helps maintain soil nutrient levels and prevents the depletion of specific nutrients.
- Cover Cropping – Growing cover crops like clover or rye between main crop cycles helps to prevent erosion and improve soil structure.
- Minimal Tillage – Reducing the frequency and intensity of soil tillage helps preserve the delicate balance of the fertile soil georgia.
These sustainable techniques, combined with precision agriculture tools and soil testing, allow Georgia’s farmers to optimize crop yields while safeguarding the long-term health of the state’s valuable soil resources.

“As a farmer, I know that the health of our soil is the foundation for a thriving, sustainable agricultural industry. That’s why we’re committed to using the latest conservation practices to protect and nurture the land that has sustained our families for generations.”
– Herbert Hodges, 2024 Georgia Conservationist of the Year
Environmental Impact of Georgia’s Soil
Georgia’s red clay soil is key to its ecosystems, supporting plants and animals. But, it also has big environmental effects that need careful handling and conservation.
Effects on Local Ecosystems
The red clay soil in Georgia is rich in nutrients, helping diverse habitats thrive. It also drains well, keeping streams, rivers, and wetlands healthy. Yet, erosion and runoff can harm water quality, affecting aquatic life and the natural balance.
Soil Conservation Efforts
Many groups and agencies work to save Georgia’s soil. The Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission leads these efforts. They aim to stop erosion, keep soil healthy, and protect watersheds. They use methods like cover cropping and no-till farming to keep the soil safe.
By understanding and supporting soil conservation, we protect Georgia’s beauty and ecosystems. This ensures a sustainable future for farming and recreation in the state.
| Key Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Vidalia Onion Industry Farm Gate Value (2022) | $200 million |
| Vidalia Onion Growing Region | 20 counties surrounding Vidalia, Georgia |
| Proposed Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge Expansion | Approximately 22,000 acres |
| Okefenokee Swamp Eco-tourism Industry Value | $64 million |
| Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge Annual Visitors | Over 725,000 |
“The Georgia Conservancy supported the proposed boundary expansion for the Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge by submitting public comments to the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service on November 18.”
The future of georgia soil types and georgia soil management is vital. It’s crucial for Georgia’s ecosystems, agriculture, and natural beauty, attracting visitors worldwide.
Geology and Formation of Georgian Soil
Georgia’s soil types vary due to its unique geology and climate. The georgia red hills soil is shaped by weathering over millions of years. This process has molded the landscape.
Role of Weathering Processes
The soil composition georgia comes from weathering bedrock. In the north, granite and gneiss rocks create nutrient-rich soils. These rocks break down, releasing minerals that make the soil fertile.
Influence of Climate on Soil Types
Georgia’s warm, humid climate shapes its soil types. The state’s climate speeds up weathering, breaking down rocks fast. This leads to nutrient-rich soil.
The georgia red hills soil gets its color from iron-rich minerals. The warm, moist environment helps oxidize these minerals. This gives the soil its reddish color.
Georgia’s geology and climate mix to create diverse soils. Each area has its own soil type. Knowing this helps us use Georgia’s soil wisely.
Comparison with Other Southern States
Georgia is famous for its red clay soil. But, other southern states have their own special soils. Let’s see how Georgia’s soil compares to its neighbors.
Soil Differences with Alabama
Alabama, like Georgia, has red clay soil. But, Alabama’s soil is more varied. It includes sandy loams, silt loams, and black belt prairie soil. This variety comes from Alabama’s different landscapes and history.
Unique Soil Features of South Carolina
South Carolina is different from Georgia’s red clay. Its coastal areas have sandy, well-drained soils. The uplands have clay and loamy soils. This shows South Carolina’s varied landscapes, from sandy plains to mountains.
| Soil Characteristics | Georgia | Alabama | South Carolina |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant Soil Type | Red Clay | Varied (Red Clay, Sandy Loam, Silt Loam) | Sandy Coastal, Clay/Loamy Upland |
| Geological Formation | Piedmont and Coastal Plain | Diverse Topography | Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge |
| Drainage | Moderate to Poor | Varies by Soil Type | Sandy Soils: Well-Drained, Clay/Loam: Moderate |
Each state’s soil is shaped by its unique history and environment. This makes the American South’s farming landscape very diverse.
Cultural Impact of Georgia’s Soil
Georgia’s red clay soil has deeply influenced the state’s culture. It shapes its food and art. This soil, formed over centuries, is a symbol of Georgian identity.
Role in Southern Cuisine
The red clay soil in Georgia is perfect for growing many foods. It’s known for its good drainage and nutrients. This makes peaches, peanuts, and pecans taste special.
Cornbread gets its unique taste and color from this soil. It’s a key part of Southern cooking.
Influence on Local Art and Music
The red-orange color of Georgia’s soil inspires artists. Painters, potters, and craftspeople use it in their work.
“The red clay of Georgia is not just a physical reality, but a canvas for artistic expression, a medium that connects us to the land and our cultural heritage.”
– Jane Doe, local artist. The soil also influences music in Georgia. Songs often mention “red dirt” and “red clay,” celebrating the state’s beauty.
Georgia’s red clay soil has a big impact on its culture. It shapes food, inspires art, and is a part of music. This shows how important the land is to Georgia’s identity.
Future of Soil Management in Georgia
Georgia’s red clay soil is facing big challenges from urban growth and industry. But, researchers and communities are working hard to protect this valuable resource. They are finding new ways to manage soil and getting people involved in keeping it healthy.
Advances in Soil Research
At places like Kennesaw State University, scientists are leading the way in soil science. They are using new technologies like precision agriculture and soil sensors. These tools help farmers use soil better, manage nutrients, and fight climate change.
These experts are finding the best ways to care for Georgia’s soil. They aim to improve soil management and agriculture in the state.
Community Initiatives for Soil Health
In Georgia, people are coming together to protect the soil. Urban gardens and forestry programs are making cities greener and more food secure. These efforts teach people about the importance of healthy soil for strong communities.
FAQ
What is Georgia’s red clay soil?
Georgia’s red clay soil is a key part of the state’s landscape. It has a deep red color and lots of clay. This soil comes from iron-rich rocks and minerals weathered over millions of years. It’s most common in the Piedmont region of Georgia.
What are the characteristics of Georgia’s red clay soil?
This soil is made of fine particles that hold water well but can get compacted. It’s acidic and full of minerals like iron and aluminum.
How did Georgia’s red clay soil impact early settlement and agriculture?
Native Americans used this soil for crops like corn and beans. But early settlers found it hard to adapt to. The soil’s fertility and moisture retention shaped early agriculture and settlement patterns.
What other types of soil are found in Georgia?
Georgia has different soils in different areas. Sandy soil is common near the coast, perfect for peanuts. The Piedmont has the famous red clay. Northern mountains have a mix of clay and rocky soils. Each supports unique ecosystems and farming methods.
What are the benefits of Georgia’s red clay soil?
This soil holds water well, cutting down on watering needs. It’s also fertile for certain crops. The soil’s minerals are good for plant growth.
What are the challenges of working with Georgia’s red clay soil?
This soil can erode easily, especially on slopes. It might lack nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen. It can also compact, causing drainage and root growth issues. Managing the soil well is key.
How can gardeners and farmers successfully grow in Georgia’s red clay soil?
Gardeners often add organic matter to improve the soil. Raised beds and containers are good strategies. Choosing plants that like clay soil is important. Good drainage and aeration are crucial for plant health. Sustainable farming practices help keep the soil healthy.
How does Georgia’s red clay soil influence the local environment and culture?
The soil supports unique plants and animals. Erosion can harm water quality. Conservation efforts aim to prevent erosion and protect watersheds. The soil’s color and texture inspire artists and craftspeople. It’s also mentioned in local music and literature, showing the region’s bond with the land.










1 thought on “Georgia’s Famous Red Clay Soil: A Complete Guide”